MIND Your Diet for Better Brain Health
Some people follow a specific diet to lose weight, while others follow a diet to lower blood pressure or improve heart health. However, there’s one diet that has the potential to provide all those benefits plus delay or reduce the onset of cognitive decline: The MIND diet.
The MIND diet is a dietary program specifically designed for Neurodegenerative delay. This was formed by blending 2 highly effective diets: the Mediterranean and Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet.
The Mediterranean diet mainly focuses on a heart-healthy eating plan. The DASH diet aims to treat or prevent high blood pressure.
The MIND diet is different because it is designed to target brain health and reduce the risk of some neurological diseases such as dementia. The MIND diet encourages the consumption of a variety of foods that ultimately benefit both the nervous system and cognitive health.
At Aviv Clinics Dubai by DP World, our clinical team includes dietetic support for every client due to the important role of nutrition when it comes to cognitive and neurological health.
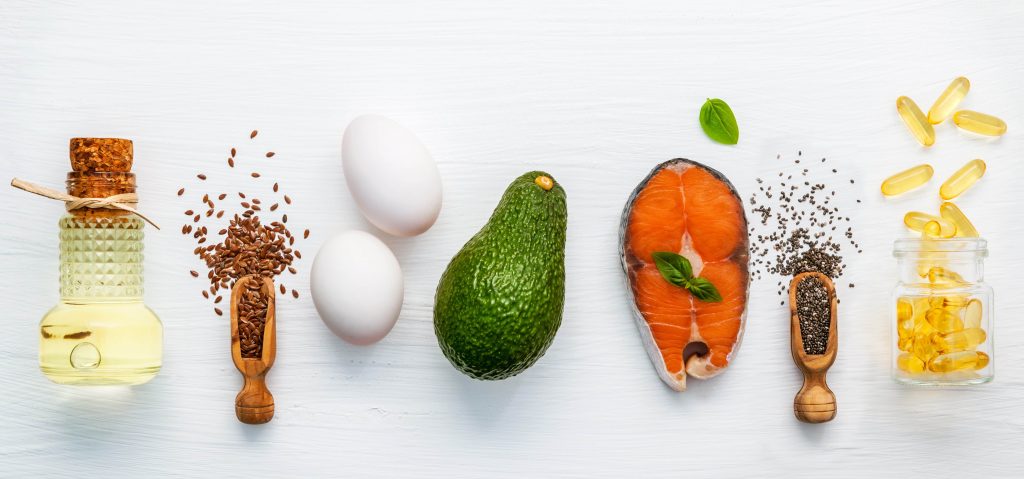

Essentials for the Brain
For optimal health, your brain needs specific nutrients such as
- Omega-3 fatty acids for strengthening brain cell structure
- Choline to help regulate memory, mood, and cognitive performance
- Flavonoids for regulating inflammation and improving blood flow
- Vitamin E for protection against inflammation
The MIND diet provides all of the above mentioned essential nutrients. The diet omits or limits foods with ingredients that could negatively impact the brain, like saturated fats and trans fats, which are believed to be responsible for increasing beta-amyloid protein levels in the brain. This protein accumulates in the brain and can disrupt communication between brain cells and ultimately lead to brain cell death.
Eating foods that contain these unhealthy fats have been associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Examples of foods containing unhealthy fats are red meats, processed foods, and fried foods.
Foods containing antioxidants and vitamins—like what’s suggested as part of the MIND diet—may prevent the formation of these beta-amyloid plaques in the brain. Plant-based foods also contain phytonutrients and antioxidants which is beneficial for overall health.
More than half of your brain is made up of omega-3 fats. Your body needs foods rich in omega-3 fats to provide the necessary protective anti-inflammatory benefits. Omega-3 foods includes
Healthy fats, known as polyunsaturated fats, found in fish oils, flax seed, walnuts, and cold-water fish for example, and monounsaturated fats, which have anti-inflammatory properties, obtained from eating avocado, nuts, and seeds, all provide the essential omega-3 fatty acids that are beneficial for optimal brain health.

How to Make the MIND Diet Work for You
The MIND diet encourages a diversity of healthy foods designed to deliver a multitude of brain health benefits. It includes foods rich in phytonutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants such as:
- Leafy Greens and Vegetables: eat at least 1 serving of leafy greens e.g. spinach every day.
- Berries: they are particularly emphasized in the MIND Diet due to their potential cognitive benefits. Aim for at least 2-3 servings weekly.
- Nuts: vary the type of nuts you eat to gain the most benefit. One serving of nuts equates to one handful or roughly 30 grams.
- Olive oil and olives
- Whole grain: Oatmeal, quinoa, brown rice, whole-wheat pasta, and 100% whole-wheat bread.
- Fish: Choose fatty fish like salmon, sardines, trout, tuna, and mackerel for their high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. Aim to have oily fish once weekly and white fish once weekly.
- Beans, lentils and soybeans.
- Poultry: chicken, turkey.
- Stay hydrated.
Other tips include cooking at home to have better control over the ingredients and cooking methods. Also, be mindful of your portion sizes and create a meal plan to make it easier to adhere to the diet.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
- Butter and margarine: limit your intake to less than one tablespoon daily.
- Cheese: if you have cheese, the best options are the white cheeses such as feta/Greek cheese, halloumi, cottage cheese.
- Red meat: aim for no more than two servings each week.
- Fried food: the MIND diet highly discourages fried food, especially from fast-food restaurants. Limit consumption to a maximum of once weekly.
- Pastries and sweets: limit your intake to a couple of times a week.

The Bottom Line
Researchers are learning more and more about the link between cognition and the MIND diet. Please keep in mind, the MIND Diet is not a guarantee against cognitive decline or neurodegenerative diseases, but it may help reduce your risk and promote overall health. As you age and the risk of developing memory disorders like dementia increase, laying a firm foundation for healthier eating will become vital to maintaining quality of life.
As leaders in brain performance, the expert clinicians at Aviv Clinics Dubai help keep your mind and body healthy for years to come. With hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) at its core, cognitive and physical training, and nutrition coaching, the ground-breaking Aviv Medical Program enhances cognitive and physical function and triggers the body’s natural capabilities at self-regeneration.
Contact us for a free consultation and learn about how our nutritional coaching will enhance the benefits of the Aviv Medical Program.
The Effect of Coffee on Brain Health
Pour-over, solo, drip, French-pressed – however you enjoy your coffee, it may be doing more for you than just getting you going in the morning. Drinking coffee may also protect you from a variety of health conditions, so long as it is consumed in moderation.
For decades, coffee had a poor reputation because of early studies that deemed it a carcinogen and linked it to an increased risk for heart disease. Recent research now suggests that drinking coffee, including decaffeinated coffee, may actually provide a variety of health benefits when consumed in moderation.
The Benefits of Coffee on Brain Health
Some of coffee’s health benefits are commonly known, including that it boosts metabolism and increases energy levels. Lesser known, but perhaps more important benefits of coffee are that it also:
- Enhances brain function
- Lowers the risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease
- Decreases the risk of stroke and depression.
Beyond brain health, moderate consumption of coffee also helps reduce the risk of some cancers, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Coffee’s Key Ingredients
Caffeine is just one of about 1,000 chemicals found in coffee beans, but is the best known. A stimulant, caffeine delivers a boost of energy and helps provide focus. It locks into the adenosine receptors in the brain, which cause drowsiness, and counteracts the sleepiness response by blocking the function of the receptors. Instead of feeling drowsy, caffeine stimulates the brain’s production of norepinephrine and dopamine, which is what leads to increased focus and alertness.
In addition to caffeine, coffee also contains beneficial polyphenols and antioxidants, which fight inflammation and protect against some diseases.
Polyphenols are organic compounds found in the coffee plant. They contain anti-inflammatory properties that have the potential to prevent or reduce the risk of certain cancers and other chronic health conditions. Some polyphenols may also protect against neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. Consuming polyphenols also may help regulate metabolism, weight, and cell production.
Other beneficial components in coffee include vitamin B2 (riboflavin); vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid); vitamin B1 (thiamine); vitamin B3 (niacin); folate, manganese, potassium, magnesium; and phosphorus.
Coffee beans also are enriched so that when they are ground, blended, and consumed, provide some pre- and probiotic properties for good gut health.

The Cons of Drinking Coffee
While coffee has many health benefits, it can also have some negative effects. For example, it can:
- Disrupt sleep
- Cause anxiety and jitteriness
- Lead to an addiction to caffeine
- Cause withdrawal symptoms (headache, fatigue, brain fog, and irritability) when abstaining
- Increase feelings of anxiety and agitation in those with anxiety disorders
Moderating consumption is key to enjoying its benefits.
How Much Coffee Should You Drink?
As with most foods, coffee is a healthy beverage when consumed in moderation. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends no more than five cups a day or on average 400 mg of caffeine. Another reason for moderate consumption is because too much, especially after mid-day, could interfere with getting a good night’s sleep and may create feelings of anxiety.
Optimizing the Benefits of Coffee
While coffee has many health benefits, adding refined sugar, artificial sweeteners, and/or creamers add calories and create an unhealthy beverage.
“The extra calories, sugar, and saturated fat in a coffee house beverage loaded with whipped cream and flavored syrup might offset any health benefits found in a basic black coffee.” – Harvard School of Public Health
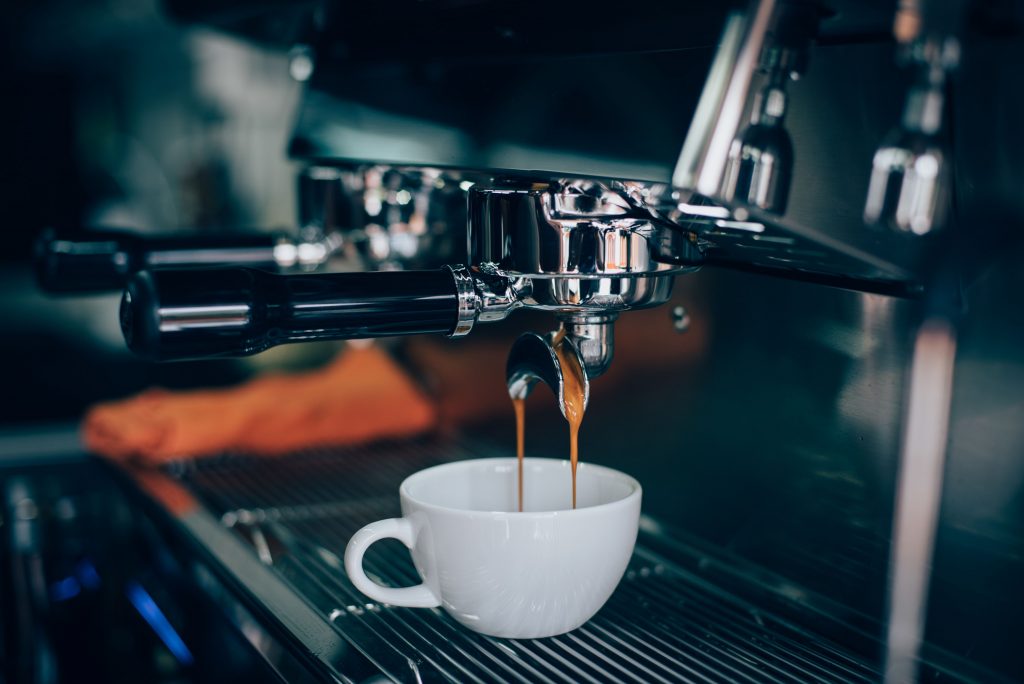

How you brew your coffee also affects the health benefits it imparts.
For example, using a paper filter or checking coffee pods for built-in filters helps prevent the passage of unhealthy chemicals present in coffee as it filters. Some of these chemicals can raise levels of LDL, or the “bad” cholesterol.
The Bottom Line
Coffee has many health benefits, when drunk in moderation. Using high quality beans, brewing it with a paper filter, and limiting additions such as refined sugars and creamers, can optimize the impact of coffee on your brain health.
Aviv Clinics Dubai – brought to you by DP World delivers a highly effective, science-based treatment protocol to enhance overall brain performance, extend healthspan, and improve the cognitive and physical symptoms of conditions such as mild cognitive decline, fibromyalgia, and Lyme disease. The Aviv Medical Program’s intensive treatment protocol uses hyperbaric oxygen therapy and includes nutrition management and dietitian support to optimize your diet for better brain health. Based on over a decade of research and development, the Aviv Medical Program is comprehensive and customized to your needs.
Contact us to learn more.
The Effect of Intermittent Fasting on Your Brain
There’s a lot of debate in the health and wellness sphere about the best diet for your health. Where some swear by low-carb high-fat diets, others insist that high-carb low-fat is the only way to eat. With so many conflicting opinions, it’s difficult to know whom to trust or what to listen to. Fortunately, there is a way you can eat that may help you lose weight, improve your brain health, and even increase your longevity, all without strict dietary restrictions. Best of all, it’s not a “diet” at all!
This “non-diet” is intermittent fasting, which is quickly building up steam in the dietary community. Unlike fad diets, fasting is more than just a passing trend because it’s as old as humanity itself. Our bodies are designed to fast, and you already do it every day. From the time you eat your last meal at night, to the time you eat breakfast in the morning, you’re fasting. Intermittent fasting is about gradually pushing out this window until your brain and body start reaping the benefits.
As a center dedicated to improving brain health and performance, Aviv Clinics understands the importance of proper nutrition and its direct effect on cognitive and physical functioning. Making dietary changes, such as Intermittent fasting, benefits brain health, promotes weight loss, and prevents certain diseases. Here’s more on intermittent fasting, along with how you can start fasting yourself.

What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is an eating style that involves alternating between periods of eating and fasting.
Intermittent fasting is not a diet; it’s a lifestyle. You’re in charge of your own meal plan, and you can customize it to your liking. You can combine intermittent fasting with the Mediterranean diet, Paleo, Keto, DASH, or any other diets. If you don’t want to follow a particular diet, just make sure that you make healthy food choices. Try to avoid artificial ingredients or overly processed foods. So long as you meet all your nutritional requirements within your eating window, just about anything goes!
Because you’re not tied down by the restrictions of a traditional diet, you have the freedom to customize your meals to your own preferences. This means that you’re more likely to stick to a consistent diet plan, which is essential if you want to lose weight and keep it off.
Is intermittent fasting healthy?
Although conventional advice would have us believe that we need to eat every 2-3 hours to sustain ourselves, our evolutionary history paints a different picture. Our hunting and gathering ancestors didn’t have regular access to food like we do, so their bodies had to develop a way to operate without a consistent source of glucose. That’s where fasting comes in as a survival mechanism.
In the same way that you might clean your home and throw out the things you don’t need, fasting is our body’s way of cleaning up shop. Fasting for extended periods allows your body to cleanse itself and use up leftover nutrients from the previous day’s meals, which triggers a process called “metabolic switching”.
Metabolic switching slows the aging and disease processes and promotes weight loss in obese individuals. Fasting also prevents breast cancer in both women and men, and studies suggest that it may improve longevity. Eating constantly doesn’t allow the body time to properly rest, which means you won’t experience the cleansing benefits of metabolic switching.
What fasting does to the brain?
Intermittent fasting is amazing for maintaining brain health. In addition to slowing the aging process, metabolic switching increases neuroplasticity in the brain. This helps optimize brain function and increase the brain’s resistance to injury and disease. Intermittent fasting also triggers a process called autophagy, which works to ward off Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s.
Fasting can also clear brain fog and sharpen the mind. Many people who fast report clearer thinking and improved moods, which can benefit your brain-gut connection and increase your overall happiness.
Intermittent Fasting for Beginners
There are a few different ways to practice intermittent fasting.
Some of the most common methods include:
Time-restricted fasting
This is the most common method of fasting, and the one most people will end up practicing. It works by limiting the daily window where you eat your food every day. For example, if you eat your first meal of the day at 10 am and your last meal at 6 pm, then you’ve fasted for 16 hours and eaten for 8, meaning that you followed a 16:8 fasting schedule. Common ratios for time-restricted fasting include 14:10, 16:8, 18:6 and 20:4.
5:2 Fasting
This method of fasting involves eating normally for 5 days a week and fasting for two. On fast days, you’ll eat one 500 calorie meal if you’re a woman, or one 600 calorie meal if you’re a man.
Alternate Day Fasting
This is a more extreme version of 5:2 fasting. Instead of fasting for only two days a week, you’ll fast on alternating days, following the same 500-600 plan for meals on fast days.
Start with time-restricted fasting before trying the more advanced options. Just like you can’t expect to run a marathon without experience, you can’t expect to fast for hours on end without a little training first.
Try gradually shrinking your eating window every day until you’ve reached your goal. If you currently eat your first meal at 8:00 am, try pushing it out to 9:00 am and eventually to 10:00 am or 11:00 am. Or if you want to try 5:2 fasting, start out by fasting only one day a week and gradually upping it to two. Whatever fasting schedule you choose, just try to be consistent. Establishing a routine and sticking to it helps establish consistency, which is key for a healthy lifestyle.
What constitutes breaking a fast?
If you’re interested in giving fasting a try, you might be wondering about what counts as breaking a fast.
Will your morning cup of coffee ruin your fasting schedule or not? The answer is, it depends.
While calorie-free beverages like coffee or tea are all right to drink while fasting, anything that has calories in it breaks a fast. That includes any kind of artificial sweeteners or creamers you may add to your favorite drink.
That doesn’t mean that you have to drink black coffee exclusively, however. You can make a game out of adding creamer to your coffee at a later time every day. Try challenging your family members or friends to see who can hold out with black coffee the longest!
Is there anyone who shouldn’t fast?
People with Type 1 diabetes or anyone who takes insulin shouldn’t fast. This can put you at risk for dangerous blood sugar problems like hypoglycemia or ketoacidosis. People with hypertension, blood pressure problems, or cognitive impairments shouldn’t fast either, and neither should anyone who struggles with remembering to eat on a daily basis.
Certain medications may also prevent people from fasting, and those who use canes or wheelchairs should also take care not to fast. As with any diet, check with your healthcare provider if you’re not sure that fasting is right for you.
Conclusion
The benefits of intermittent fasting are numerous and clear. It can increase your lifespan, lower your risks for diseases and improve your brain’s overall health. But perhaps fasting’s biggest benefit is that it allows you to put the joy back in eating. When you don’t have to worry about weighing, counting or measuring, you can focus on eating foods that nourish not only your body, but also your soul.
You can still indulge in your family’s traditional recipes without feeling guilty. It’s important to eat a balance of foods that make you happy and foods that keep you healthy. Intermittent fasting provides you with the perfect framework for this, allowing you to live your best life possible exactly the way you want to.
DP World’s Aviv Clinics Dubai
Nutrition is an important pillar in your approach to health, especially as you age. The Aviv Medical Program utilizes a multidisciplinary approach to healthy aging, including a personalized nutrition plan based on a comprehensive assessment to address your individual needs and goals, along with hyperbaric oxygen therapy, physical training, and cognitive training.
Discover how you can take your brain health and longevity into your own hands with Aviv Clinics. Learn more today.